Home » Application
If you switched a large wind turbine on to the grid with a normal switch, the  neighbours would see a brownout (because of the current required to magnetize the generator) followed by a power peak due to the generator current surging into the grid. Another unpleasant side effect of using a "hard" switch would be to put a lot of extra wear on the gearbox, since the cut-in of the generator would work as if you all of a sudden slammed on the mechanical brake of the turbine. To prevent this situation, modern wind turbines are soft starting, i.e. they connect and disconnect gradually to the grid using thyristors, a type of semiconductor continuous switches which may be controlled electronically.
neighbours would see a brownout (because of the current required to magnetize the generator) followed by a power peak due to the generator current surging into the grid. Another unpleasant side effect of using a "hard" switch would be to put a lot of extra wear on the gearbox, since the cut-in of the generator would work as if you all of a sudden slammed on the mechanical brake of the turbine. To prevent this situation, modern wind turbines are soft starting, i.e. they connect and disconnect gradually to the grid using thyristors, a type of semiconductor continuous switches which may be controlled electronically.
 neighbours would see a brownout (because of the current required to magnetize the generator) followed by a power peak due to the generator current surging into the grid. Another unpleasant side effect of using a "hard" switch would be to put a lot of extra wear on the gearbox, since the cut-in of the generator would work as if you all of a sudden slammed on the mechanical brake of the turbine. To prevent this situation, modern wind turbines are soft starting, i.e. they connect and disconnect gradually to the grid using thyristors, a type of semiconductor continuous switches which may be controlled electronically.
neighbours would see a brownout (because of the current required to magnetize the generator) followed by a power peak due to the generator current surging into the grid. Another unpleasant side effect of using a "hard" switch would be to put a lot of extra wear on the gearbox, since the cut-in of the generator would work as if you all of a sudden slammed on the mechanical brake of the turbine. To prevent this situation, modern wind turbines are soft starting, i.e. they connect and disconnect gradually to the grid using thyristors, a type of semiconductor continuous switches which may be controlled electronically.
The majority of irrigation pumping in Nebraska uses fossil fuels such as diesel, nature gas, and propane. An increasing percentage of irrigation pumping is however done by using electrical energy (42% at present).  High fuel cost is helping to drive the installed pumping systems to become electric. Wind power as a source for irrigation load becomes attractive due to the large resource of wind available in the state and the decreasing costs of wind energy. This analysis envisions using wind energy to pump water and deliver it to a storage tank connected with pivot-type irrigation system. First goal is to satisfy agriculture needs during irrigation season (spring and summer) and the second goal is to sell back excess electricity to the utility, particularly during the fall and winter months.
High fuel cost is helping to drive the installed pumping systems to become electric. Wind power as a source for irrigation load becomes attractive due to the large resource of wind available in the state and the decreasing costs of wind energy. This analysis envisions using wind energy to pump water and deliver it to a storage tank connected with pivot-type irrigation system. First goal is to satisfy agriculture needs during irrigation season (spring and summer) and the second goal is to sell back excess electricity to the utility, particularly during the fall and winter months.
 High fuel cost is helping to drive the installed pumping systems to become electric. Wind power as a source for irrigation load becomes attractive due to the large resource of wind available in the state and the decreasing costs of wind energy. This analysis envisions using wind energy to pump water and deliver it to a storage tank connected with pivot-type irrigation system. First goal is to satisfy agriculture needs during irrigation season (spring and summer) and the second goal is to sell back excess electricity to the utility, particularly during the fall and winter months.
High fuel cost is helping to drive the installed pumping systems to become electric. Wind power as a source for irrigation load becomes attractive due to the large resource of wind available in the state and the decreasing costs of wind energy. This analysis envisions using wind energy to pump water and deliver it to a storage tank connected with pivot-type irrigation system. First goal is to satisfy agriculture needs during irrigation season (spring and summer) and the second goal is to sell back excess electricity to the utility, particularly during the fall and winter months.
One of the notable characteristics in the wind power generation is its uncertainty due to the sudden change in both wind speed and direction, especially for off-grid wind power generation systems. Therefore, the power output from wind turbines fluctuates from time to time. When wind turbines are connected to a small or isolated grid, the power output from other generators must be varied in response to these variations and fluctuation in order to keep system frequency and voltage within predefined limits. For this purpose, it is beneficial to integrate wind and other complementary energy sources to form hybrid power systems for assuring the stability and reliability of power supply and reducing the requirement for the wind energy storage.
Therefore, the power output from wind turbines fluctuates from time to time. When wind turbines are connected to a small or isolated grid, the power output from other generators must be varied in response to these variations and fluctuation in order to keep system frequency and voltage within predefined limits. For this purpose, it is beneficial to integrate wind and other complementary energy sources to form hybrid power systems for assuring the stability and reliability of power supply and reducing the requirement for the wind energy storage.
 Therefore, the power output from wind turbines fluctuates from time to time. When wind turbines are connected to a small or isolated grid, the power output from other generators must be varied in response to these variations and fluctuation in order to keep system frequency and voltage within predefined limits. For this purpose, it is beneficial to integrate wind and other complementary energy sources to form hybrid power systems for assuring the stability and reliability of power supply and reducing the requirement for the wind energy storage.
Therefore, the power output from wind turbines fluctuates from time to time. When wind turbines are connected to a small or isolated grid, the power output from other generators must be varied in response to these variations and fluctuation in order to keep system frequency and voltage within predefined limits. For this purpose, it is beneficial to integrate wind and other complementary energy sources to form hybrid power systems for assuring the stability and reliability of power supply and reducing the requirement for the wind energy storage.
The first heyday of wind power in America lasted from 1870 to 1930, when thousands of farmers used the wind to pump water and generate power. The second heyday is just beginning. Wind power is the fastest growing energy source in the world, with annual average growth of 32 percent between 1998 and 2002. I n the United States alone, nearly two billion dollars' worth of wind turbines are projected to come on line in 2003—enough to power 800,000 homes. The U.S.Department of Energy's (DOE) "Wind Powering America"initiative has set a goal of producing five percent of the nation's electricity from wind by 2020. DOE projects meant to achieve this goal will provide $60 billion in capital investment to rural America,$1.2 billion in new income to farmers and rural landowners,and 80,000 new jobs during the next 20 years.
n the United States alone, nearly two billion dollars' worth of wind turbines are projected to come on line in 2003—enough to power 800,000 homes. The U.S.Department of Energy's (DOE) "Wind Powering America"initiative has set a goal of producing five percent of the nation's electricity from wind by 2020. DOE projects meant to achieve this goal will provide $60 billion in capital investment to rural America,$1.2 billion in new income to farmers and rural landowners,and 80,000 new jobs during the next 20 years.
 n the United States alone, nearly two billion dollars' worth of wind turbines are projected to come on line in 2003—enough to power 800,000 homes. The U.S.Department of Energy's (DOE) "Wind Powering America"initiative has set a goal of producing five percent of the nation's electricity from wind by 2020. DOE projects meant to achieve this goal will provide $60 billion in capital investment to rural America,$1.2 billion in new income to farmers and rural landowners,and 80,000 new jobs during the next 20 years.
n the United States alone, nearly two billion dollars' worth of wind turbines are projected to come on line in 2003—enough to power 800,000 homes. The U.S.Department of Energy's (DOE) "Wind Powering America"initiative has set a goal of producing five percent of the nation's electricity from wind by 2020. DOE projects meant to achieve this goal will provide $60 billion in capital investment to rural America,$1.2 billion in new income to farmers and rural landowners,and 80,000 new jobs during the next 20 years.
Modern, commercial grid-connected  wind turbines have evolved from small, simple machines to large,highly sophisticated devices. Scientific and engineering expertise and advances, as well as improved computational tools, design standards, manufacturing methods, and O&M procedures, have all supported these technology developments. Onshore wind energy technologies are already being manufactured and deployed on a commercial basis, and are expected to further reduce the cost of wind energy while enhancing system and component performance and reliability.
wind turbines have evolved from small, simple machines to large,highly sophisticated devices. Scientific and engineering expertise and advances, as well as improved computational tools, design standards, manufacturing methods, and O&M procedures, have all supported these technology developments. Onshore wind energy technologies are already being manufactured and deployed on a commercial basis, and are expected to further reduce the cost of wind energy while enhancing system and component performance and reliability.
 wind turbines have evolved from small, simple machines to large,highly sophisticated devices. Scientific and engineering expertise and advances, as well as improved computational tools, design standards, manufacturing methods, and O&M procedures, have all supported these technology developments. Onshore wind energy technologies are already being manufactured and deployed on a commercial basis, and are expected to further reduce the cost of wind energy while enhancing system and component performance and reliability.
wind turbines have evolved from small, simple machines to large,highly sophisticated devices. Scientific and engineering expertise and advances, as well as improved computational tools, design standards, manufacturing methods, and O&M procedures, have all supported these technology developments. Onshore wind energy technologies are already being manufactured and deployed on a commercial basis, and are expected to further reduce the cost of wind energy while enhancing system and component performance and reliability.
With the development of science and technology, energy storage is one of the most effective ways to solve the problem of wind power grid connection.  At present, there are many kinds of energy storage technologies in wind power system, and their functions and functions are quite different. The selection of energy storage forms should be based on the different requirements of wind farms and the benefits of energy storage system for wind power system. The application of energy storage technology in wind power generation system greatly improves the utilization rate of power resources and meets people's demand for power resources to the greatest extent.
At present, there are many kinds of energy storage technologies in wind power system, and their functions and functions are quite different. The selection of energy storage forms should be based on the different requirements of wind farms and the benefits of energy storage system for wind power system. The application of energy storage technology in wind power generation system greatly improves the utilization rate of power resources and meets people's demand for power resources to the greatest extent.
 At present, there are many kinds of energy storage technologies in wind power system, and their functions and functions are quite different. The selection of energy storage forms should be based on the different requirements of wind farms and the benefits of energy storage system for wind power system. The application of energy storage technology in wind power generation system greatly improves the utilization rate of power resources and meets people's demand for power resources to the greatest extent.
At present, there are many kinds of energy storage technologies in wind power system, and their functions and functions are quite different. The selection of energy storage forms should be based on the different requirements of wind farms and the benefits of energy storage system for wind power system. The application of energy storage technology in wind power generation system greatly improves the utilization rate of power resources and meets people's demand for power resources to the greatest extent.  Small-scale wind energy is a small but rapidly growing segment of the RE industry in the US. Like other renewable sources, in its initial stage, the cost of small wind electricity is generally less competitive when compared to current market prices of traditional energy sources. Thus, in an effort to support RE development, many US states have adopted a variety of policies to encourage small wind power. This is in line with the oft-cited idea of states serving as “laboratories of democracy” to experiment with a variety of policy tools.
Small-scale wind energy is a small but rapidly growing segment of the RE industry in the US. Like other renewable sources, in its initial stage, the cost of small wind electricity is generally less competitive when compared to current market prices of traditional energy sources. Thus, in an effort to support RE development, many US states have adopted a variety of policies to encourage small wind power. This is in line with the oft-cited idea of states serving as “laboratories of democracy” to experiment with a variety of policy tools.
The livelihood and well-being of people, animals, and crops depends on a reliable, cost-effective supply of clean water.  Mechanical wind water pumping machines have been used to pump water from wells for centuries. The technology of modern mechanical water pumpers is relatively simple, the maintenance requirements are modest, and the replacement parts are not difficult to obtain. The mechanical water pumper is the best option in some circumstances. However, because it must be placed close to the water source, it is often unable to capture the best wind resources.
Mechanical wind water pumping machines have been used to pump water from wells for centuries. The technology of modern mechanical water pumpers is relatively simple, the maintenance requirements are modest, and the replacement parts are not difficult to obtain. The mechanical water pumper is the best option in some circumstances. However, because it must be placed close to the water source, it is often unable to capture the best wind resources.
 Mechanical wind water pumping machines have been used to pump water from wells for centuries. The technology of modern mechanical water pumpers is relatively simple, the maintenance requirements are modest, and the replacement parts are not difficult to obtain. The mechanical water pumper is the best option in some circumstances. However, because it must be placed close to the water source, it is often unable to capture the best wind resources.
Mechanical wind water pumping machines have been used to pump water from wells for centuries. The technology of modern mechanical water pumpers is relatively simple, the maintenance requirements are modest, and the replacement parts are not difficult to obtain. The mechanical water pumper is the best option in some circumstances. However, because it must be placed close to the water source, it is often unable to capture the best wind resources.
Wind is used to produce electricity by converting the kinetic energy of air in motion into electricity.  In modern wind turbines, wind rotates the rotor blades, which convert kinetic energy into rotational energy. This rotational energy is transferred by a shaft which to the generator, thereby producing electrical energy. The use of wind energy can be traced back thousands of years to many ancient civilizations. The ancient human histories have revealed that wind energy was discovered and used independently at several sites of the earth.
In modern wind turbines, wind rotates the rotor blades, which convert kinetic energy into rotational energy. This rotational energy is transferred by a shaft which to the generator, thereby producing electrical energy. The use of wind energy can be traced back thousands of years to many ancient civilizations. The ancient human histories have revealed that wind energy was discovered and used independently at several sites of the earth.
 In modern wind turbines, wind rotates the rotor blades, which convert kinetic energy into rotational energy. This rotational energy is transferred by a shaft which to the generator, thereby producing electrical energy. The use of wind energy can be traced back thousands of years to many ancient civilizations. The ancient human histories have revealed that wind energy was discovered and used independently at several sites of the earth.
In modern wind turbines, wind rotates the rotor blades, which convert kinetic energy into rotational energy. This rotational energy is transferred by a shaft which to the generator, thereby producing electrical energy. The use of wind energy can be traced back thousands of years to many ancient civilizations. The ancient human histories have revealed that wind energy was discovered and used independently at several sites of the earth.
Operation in severe climates imposes special design considerations on wind turbines. Severe climates may include those with unusually high extreme winds, high moisture and humidity, very high or low temperatures, and lightning.
high moisture and humidity, very high or low temperatures, and lightning.
 high moisture and humidity, very high or low temperatures, and lightning.
high moisture and humidity, very high or low temperatures, and lightning. Operation in cold temperatures also raises unique design considerations. A number of wind turbines have been installed in cold weather regions of the globe, including Finland, northern Quebec, Alaska, and other cold regions of Europe and North America and in Antarctica. Experience has shown that cold weather locations can impose significant design and operating requirements on wind turbines because of sensor and turbine icing, material properties at low temperatures, permafrost, and snow.
Offshore wind energy, as the name implies, refers to electricity produced by wind turbines that are installed offshore and implicitly in the ocean (or in lakes). The last twenty years has seen a great deal of interest in this new technology.  The primary impetus for this has been the lack of available land with a good wind resource for new turbines, particularly in northern Europe.Since then, offshore wind turbines have been installed in the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, Sweden, Ireland, Germany, and China. In 2002 and 2003, the first large, utility-scale offshore farms were commissioned. The Horns Rev and Nysted wind farms, both in Denmark, were the first farms built with capacities exceeding 100 MW. As of the end of 2008, there was over 1000 MW of installed offshore wind capacity, most of it in Europe.
The primary impetus for this has been the lack of available land with a good wind resource for new turbines, particularly in northern Europe.Since then, offshore wind turbines have been installed in the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, Sweden, Ireland, Germany, and China. In 2002 and 2003, the first large, utility-scale offshore farms were commissioned. The Horns Rev and Nysted wind farms, both in Denmark, were the first farms built with capacities exceeding 100 MW. As of the end of 2008, there was over 1000 MW of installed offshore wind capacity, most of it in Europe.
 The primary impetus for this has been the lack of available land with a good wind resource for new turbines, particularly in northern Europe.Since then, offshore wind turbines have been installed in the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, Sweden, Ireland, Germany, and China. In 2002 and 2003, the first large, utility-scale offshore farms were commissioned. The Horns Rev and Nysted wind farms, both in Denmark, were the first farms built with capacities exceeding 100 MW. As of the end of 2008, there was over 1000 MW of installed offshore wind capacity, most of it in Europe.
The primary impetus for this has been the lack of available land with a good wind resource for new turbines, particularly in northern Europe.Since then, offshore wind turbines have been installed in the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, Sweden, Ireland, Germany, and China. In 2002 and 2003, the first large, utility-scale offshore farms were commissioned. The Horns Rev and Nysted wind farms, both in Denmark, were the first farms built with capacities exceeding 100 MW. As of the end of 2008, there was over 1000 MW of installed offshore wind capacity, most of it in Europe.

Featured Articles
Wind Turbine for Onshore Application
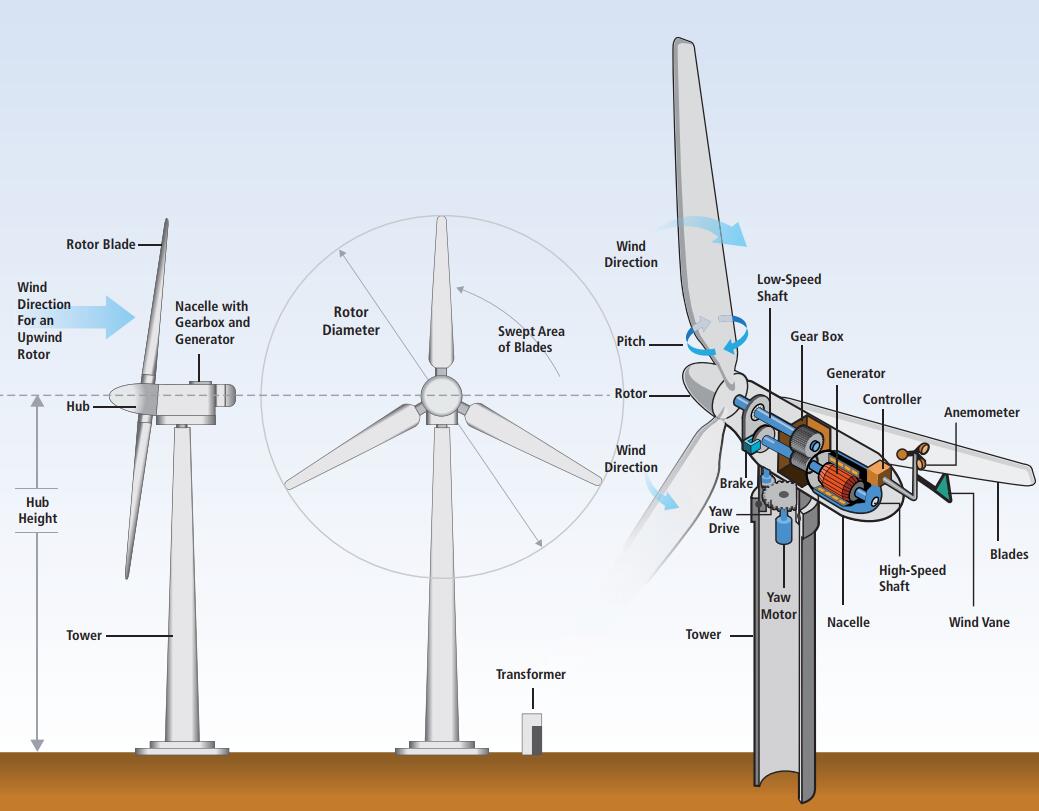 Modern, commercial grid-connected wind turbines have evolved from small, simple machines to large,highly ...
Modern, commercial grid-connected wind turbines have evolved from small, simple machines to large,highly ...
 Modern, commercial grid-connected wind turbines have evolved from small, simple machines to large,highly ...
Modern, commercial grid-connected wind turbines have evolved from small, simple machines to large,highly ...Application in Energy Storage
 With the development of science and technology, energy storage is one of the most effective ways to solve the problem of ...
With the development of science and technology, energy storage is one of the most effective ways to solve the problem of ...
 With the development of science and technology, energy storage is one of the most effective ways to solve the problem of ...
With the development of science and technology, energy storage is one of the most effective ways to solve the problem of ...Applications for Small Wind Turbines
 Small-scale wind energy is a small but rapidly growing segment of the RE industry in the US. Like other renewable sources, in its ...
Small-scale wind energy is a small but rapidly growing segment of the RE industry in the US. Like other renewable sources, in its ...
 Small-scale wind energy is a small but rapidly growing segment of the RE industry in the US. Like other renewable sources, in its ...
Small-scale wind energy is a small but rapidly growing segment of the RE industry in the US. Like other renewable sources, in its ...History of Wind Energy Applications
 Wind is used to produce electricity by converting the kinetic energy of air in motion into electricity. In modern wind ...
Wind is used to produce electricity by converting the kinetic energy of air in motion into electricity. In modern wind ...
 Wind is used to produce electricity by converting the kinetic energy of air in motion into electricity. In modern wind ...
Wind is used to produce electricity by converting the kinetic energy of air in motion into electricity. In modern wind ...Application in Severe Climates
 Operation in severe climates imposes special design considerations on wind turbines. Severe climates may include those with ...
Operation in severe climates imposes special design considerations on wind turbines. Severe climates may include those with ...
 Operation in severe climates imposes special design considerations on wind turbines. Severe climates may include those with ...
Operation in severe climates imposes special design considerations on wind turbines. Severe climates may include those with ...