Basics of Wind Farms
Throughout history, wind has been used to move grain mills or push the vessels that sailed the seas. However, it was not until well into the 19th century that the first wind turbines capable of generating electricity from the wind were made. Currently, the high potential of wind energy and its strategic value place it as one of the renewable sources called to play a decisive role among the technologies that will allow us to achieve a climate-neutral European economy by 2050.
What is a wind farm?
A wind farm, also known as a wind park, is an area of several square kilometers that houses an array of wind turbines to harness the winds from land or sea and generate electricity, which is fed into the grid for consumption.

These wind turbines work according to a very simple principle, making the most of the wind's force, which in this case acts as a source of primary energy. By spinning its blades, it produces kinetic energy and a generator then converts this kinetic energy into electrical energy.
The amount of energy that a wind farm can produce depends on the location, the size of the turbines, and the length of their blades. The capacity of wind turbines has been increasing over time, thanks to the research and development in this field. In 1985, the most common turbine model had a capacity of 0.05 megawatts (MW) and a rotor diameter of 15 meters. The large wind energy projects currently have a turbine capacity greater than 5 MW.
The continuous advances in the manufacturing and design of wind turbines, combined with the improvement in infrastructures, have managed to notably reduce the costs of wind energy and have reaffirmed its position as a key driver in the energy transition. According to WindEurope, in 2021 European wind farms generated 437 terawatt-hours (TWh) of electricity, covering 15% of demand on average, although in several countries it surpassed 20% of electricity coverage, such as in Portugal (26%), Spain (24%), and Germany (23%).
How do wind farms work?
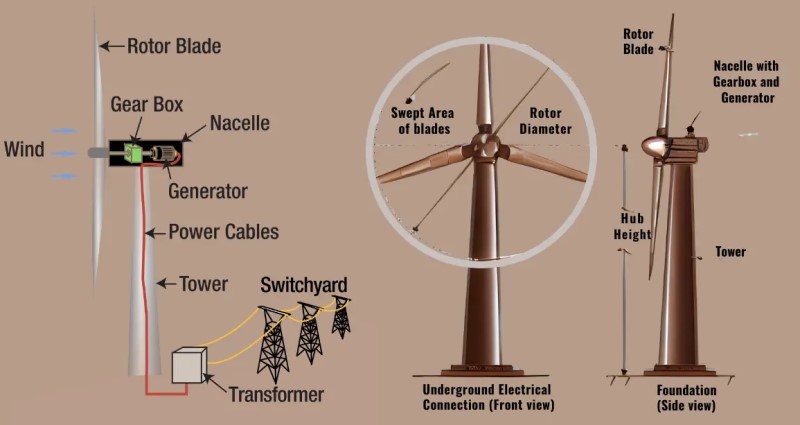 A wind turbine consists of a tower, nacelle, and a rotor on its upper part with multiple blades, pointed in the direction of the wind. The propellers turn around a horizontal axle that acts on an electricity generator. Renewable energy produced by each wind turbine is transported to ground level through underground electrical cables that carry it to the transformer of the wind power plant, tasked with redistributing it to supply the electric grid and meet the energy needs of homes and companies.
A wind turbine consists of a tower, nacelle, and a rotor on its upper part with multiple blades, pointed in the direction of the wind. The propellers turn around a horizontal axle that acts on an electricity generator. Renewable energy produced by each wind turbine is transported to ground level through underground electrical cables that carry it to the transformer of the wind power plant, tasked with redistributing it to supply the electric grid and meet the energy needs of homes and companies.
Operation of wind turbines
The operation of a wind turbine depends on a very simple mechanism. The rotor, activated by the wind, transmits its movement to a high-speed axle. This multiplier transforms the slow movement of the blades (between 18 and 25 revolutions per minute) into a faster rotation (up to 1,800 revolutions per minute) capable of driving the electric generator. The latter will be tasked with transforming the mechanical energy received into electrical energy. Wind turbines are classified generally according to the direction of the axle: Vertical Axis Wind Turbine: Its blades rotate around a central, vertical axle.
The latter will be tasked with transforming the mechanical energy received into electrical energy. Wind turbines are classified generally according to the direction of the axle: Vertical Axis Wind Turbine: Its blades rotate around a central, vertical axle.
Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine: In this case, the blades turn in a direction perpendicular to the wind speed.
Recently, a new bladeless wind turbine model, easy to install and maintain, has been launched, which adapts quicker to the changes in wind direction. The device consists of a cylinder that oscillates when the wind hits it. The movement of the cylinder generates mechanical energy that, in turn, is transformed into electricity thanks to an alternator.
Operation of the transformer (wind power plant)
Once the generator transforms the kinetic energy it receives into electricity, a transformer is used to raise the voltage (from 20 KV to 66 KV) and be able to transport the current through the wind farm. In this way, the energy is transmitted by medium voltage cables to the substation. Once there, it is converted into high voltage current (above 132 KV). Then, a power transmission line is laid that transfers the electricity to the installations connected to the distribution grid. The latter will be tasked with transporting the electricity to companies and homes.
How to decide where to install a wind farm
Wind farms are normally installed in areas where you can harness terrestrial or sea winds (thanks to the wind characteristics of the area and the site's suitability) without interfering with the environment or harming the natural habitat of species. For this reason, when choosing where to put it you have to take into account the following issues:
Types of wind farms and advantages of each one
Advantages of wind power plants
Wind power plants, also known as wind farms, are a renewable and sustainable energy source that uses wind energy to generate electricity. They offer several advantages in terms of sustainability, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
One of the major advantages of wind farms is that they use an unlimited and free source of renewable energy that will always be available. Also, they don't release greenhouse gases or other pollutants, which makes them a clean way to produce energy.
Another important advantage is that wind power plants can significantly reduce energy production costs once they're built. Moreover, they offer greater reliability and energy security given that they're more consistent and predictable and can be installed in remote or offshore locations.
Lastly, wind farms also offer environmental and health benefits by reducing the amount of greenhouse gases and other pollutants released into the atmosphere, which improves air quality in nearby communities.
What is a wind farm?
A wind farm, also known as a wind park, is an area of several square kilometers that houses an array of wind turbines to harness the winds from land or sea and generate electricity, which is fed into the grid for consumption.

These wind turbines work according to a very simple principle, making the most of the wind's force, which in this case acts as a source of primary energy. By spinning its blades, it produces kinetic energy and a generator then converts this kinetic energy into electrical energy.
The amount of energy that a wind farm can produce depends on the location, the size of the turbines, and the length of their blades. The capacity of wind turbines has been increasing over time, thanks to the research and development in this field. In 1985, the most common turbine model had a capacity of 0.05 megawatts (MW) and a rotor diameter of 15 meters. The large wind energy projects currently have a turbine capacity greater than 5 MW.
The continuous advances in the manufacturing and design of wind turbines, combined with the improvement in infrastructures, have managed to notably reduce the costs of wind energy and have reaffirmed its position as a key driver in the energy transition. According to WindEurope, in 2021 European wind farms generated 437 terawatt-hours (TWh) of electricity, covering 15% of demand on average, although in several countries it surpassed 20% of electricity coverage, such as in Portugal (26%), Spain (24%), and Germany (23%).
How do wind farms work?

Operation of wind turbines
The operation of a wind turbine depends on a very simple mechanism. The rotor, activated by the wind, transmits its movement to a high-speed axle. This multiplier transforms the slow movement of the blades (between 18 and 25 revolutions per minute) into a faster rotation (up to 1,800 revolutions per minute) capable of driving the electric generator.
 The latter will be tasked with transforming the mechanical energy received into electrical energy. Wind turbines are classified generally according to the direction of the axle: Vertical Axis Wind Turbine: Its blades rotate around a central, vertical axle.
The latter will be tasked with transforming the mechanical energy received into electrical energy. Wind turbines are classified generally according to the direction of the axle: Vertical Axis Wind Turbine: Its blades rotate around a central, vertical axle.Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine: In this case, the blades turn in a direction perpendicular to the wind speed.
Recently, a new bladeless wind turbine model, easy to install and maintain, has been launched, which adapts quicker to the changes in wind direction. The device consists of a cylinder that oscillates when the wind hits it. The movement of the cylinder generates mechanical energy that, in turn, is transformed into electricity thanks to an alternator.
Operation of the transformer (wind power plant)
Once the generator transforms the kinetic energy it receives into electricity, a transformer is used to raise the voltage (from 20 KV to 66 KV) and be able to transport the current through the wind farm. In this way, the energy is transmitted by medium voltage cables to the substation. Once there, it is converted into high voltage current (above 132 KV). Then, a power transmission line is laid that transfers the electricity to the installations connected to the distribution grid. The latter will be tasked with transporting the electricity to companies and homes.
How to decide where to install a wind farm
Wind farms are normally installed in areas where you can harness terrestrial or sea winds (thanks to the wind characteristics of the area and the site's suitability) without interfering with the environment or harming the natural habitat of species. For this reason, when choosing where to put it you have to take into account the following issues:
- Possible impact on the environment
- Intensity and frequency of wind
- Terrain and accessibility to the area
- Legal and territorial feasibility
Types of wind farms and advantages of each one
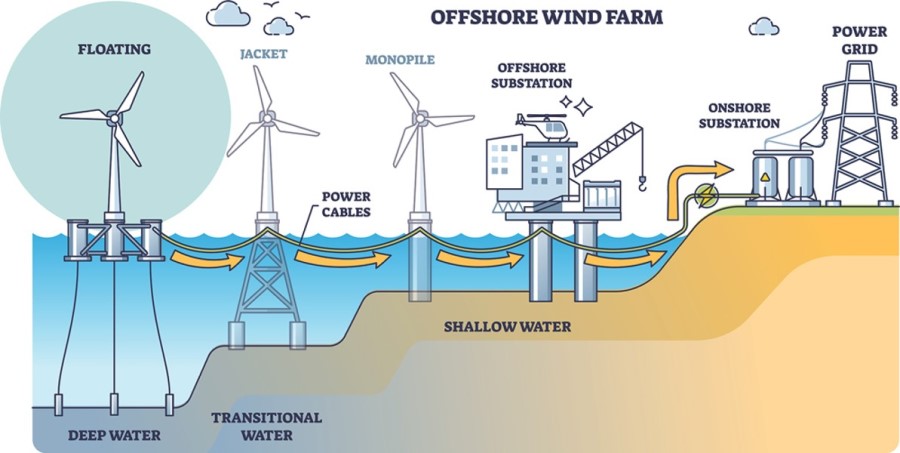
- Onshore wind farms: They are currently the most common. They are located on land no less than 3 kilometers from the coast and feed on terrestrial air currents. The advantage that this location offers is its easy accessibility and proximity to the electric grid.
- Nearshore wind farms: They are also located on land, but less than 3 kilometers from the coast. The advantage of opting for this location is that it can harness both terrestrial winds and sea winds to produce energy.
- Offshore wind farms: These structures are built in the open sea several miles from the coast. Among their main benefits compared to land installations is that the wind's force is greater, at a lower altitude, and more regular than on land.

Advantages of wind power plants
Wind power plants, also known as wind farms, are a renewable and sustainable energy source that uses wind energy to generate electricity. They offer several advantages in terms of sustainability, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
One of the major advantages of wind farms is that they use an unlimited and free source of renewable energy that will always be available. Also, they don't release greenhouse gases or other pollutants, which makes them a clean way to produce energy.
Another important advantage is that wind power plants can significantly reduce energy production costs once they're built. Moreover, they offer greater reliability and energy security given that they're more consistent and predictable and can be installed in remote or offshore locations.
Lastly, wind farms also offer environmental and health benefits by reducing the amount of greenhouse gases and other pollutants released into the atmosphere, which improves air quality in nearby communities.
Post a Comment:
You may also like:

Featured Articles
What is Wind Energy?
 Wind is moving air. We can use the energy in wind to do work. Early Egyptians used the wind to sail ships on the Nile River. ...
Wind is moving air. We can use the energy in wind to do work. Early Egyptians used the wind to sail ships on the Nile River. ...
 Wind is moving air. We can use the energy in wind to do work. Early Egyptians used the wind to sail ships on the Nile River. ...
Wind is moving air. We can use the energy in wind to do work. Early Egyptians used the wind to sail ships on the Nile River. ...Wind Farm Siting, Installation and ...
 Before wind turbines can be installed, the most appropriate location or locations for them needs to be determined. The ...
Before wind turbines can be installed, the most appropriate location or locations for them needs to be determined. The ...
 Before wind turbines can be installed, the most appropriate location or locations for them needs to be determined. The ...
Before wind turbines can be installed, the most appropriate location or locations for them needs to be determined. The ...What is a Capacity Factor?
 Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy in moving air into rotational energy, which in turn is converted to ...
Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy in moving air into rotational energy, which in turn is converted to ...
 Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy in moving air into rotational energy, which in turn is converted to ...
Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy in moving air into rotational energy, which in turn is converted to ...Basics of Wind Energy Production
 In the United States, most wind energy is commercially generated for delivery and sale on the grid. Wind projects vary in ...
In the United States, most wind energy is commercially generated for delivery and sale on the grid. Wind projects vary in ...
 In the United States, most wind energy is commercially generated for delivery and sale on the grid. Wind projects vary in ...
In the United States, most wind energy is commercially generated for delivery and sale on the grid. Wind projects vary in ...Basics of Wind Farms
 Throughout history, wind has been used to move grain mills or push the vessels that sailed the seas. However, it was not ...
Throughout history, wind has been used to move grain mills or push the vessels that sailed the seas. However, it was not ...
 Throughout history, wind has been used to move grain mills or push the vessels that sailed the seas. However, it was not ...
Throughout history, wind has been used to move grain mills or push the vessels that sailed the seas. However, it was not ...